Rainwater & Groundwater Recharge
Home / Rainwater & Groundwater Recharge
Rainwater & Groundwater Recharge
Preserving Precious Resources Through Natural Replenishment Techniques
Rainwater Harvesting


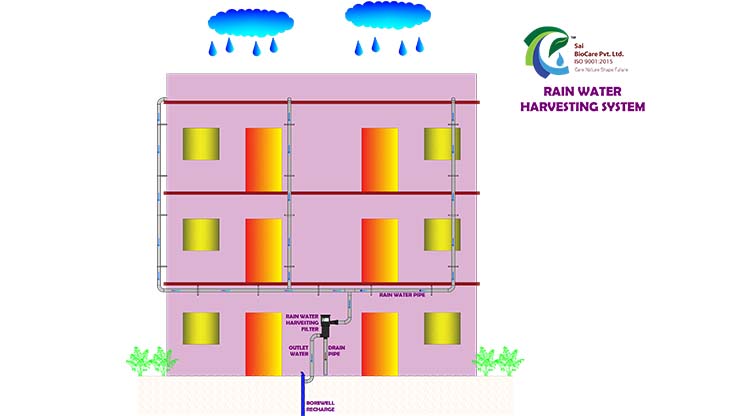


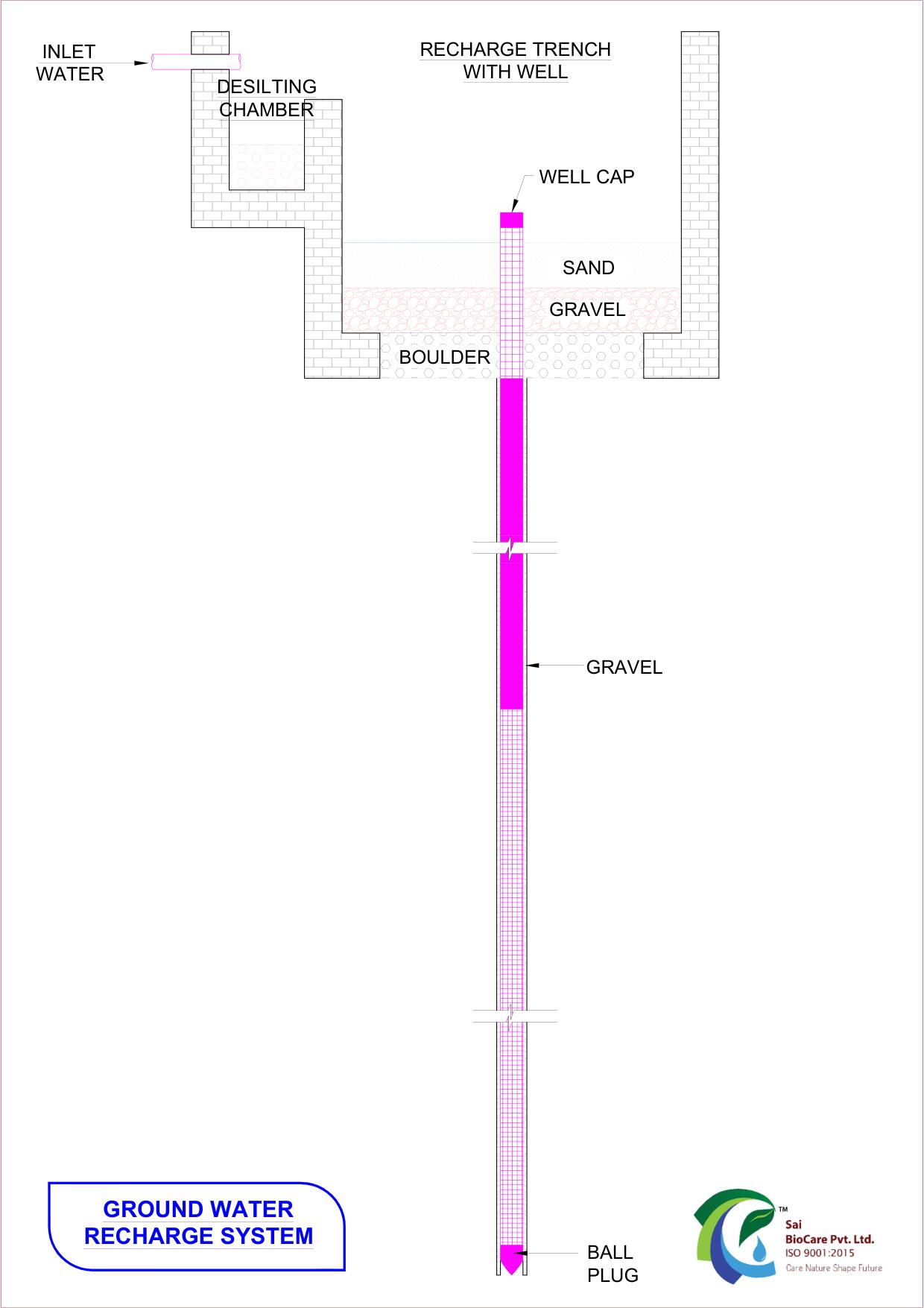
Ground Water Recharge
Groundwater recharge, also referred to as deep drainage or deep percolation, is a crucial hydrological process vital for sustaining aquifers and replenishing groundwater reserves. As water from the earth’s surface infiltrates downward through soil and permeable rock layers, it accumulates in underground aquifers. This process plays a pivotal role in areas facing significant challenges related to water resources, such as declining watersheds, soil salinization, saltwater intrusion in coastal regions, and overall water scarcity.
In regions where water and groundwater resources are heavily utilized, groundwater recharge offers a sustainable solution to mitigate these challenges. By replenishing aquifers, it helps maintain a stable groundwater level, ensuring a reliable supply of water for various purposes including agriculture, industry, and domestic use. Additionally, groundwater recharge promotes ecosystem health by sustaining surface water bodies, wetlands, and vegetation dependent on groundwater sources.
Implementing strategies to enhance groundwater recharge, such as land use management practices, artificial recharge methods, and conservation measures, becomes imperative for sustainable water management in water-stressed regions. Through these efforts, communities can alleviate the impacts of water scarcity, safeguard vital ecosystems, and ensure the long-term availability of groundwater resources for current and future generations.





















